Differences between internal and external auditing – Internal and external auditing play distinct roles in ensuring the financial health and operational efficiency of organizations. While both disciplines share the common goal of providing assurance, they differ significantly in scope, objectives, and methodologies.
This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of internal and external auditing, exploring their respective roles, responsibilities, and reporting mechanisms. By understanding these differences, stakeholders can better appreciate the value and limitations of each audit type and make informed decisions about their use.
1. Internal vs. External Auditing
Scope and Objectives
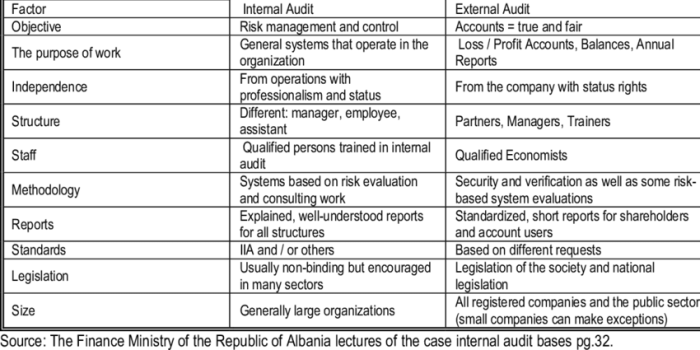
Internal auditing focuses on improving an organization’s operations and efficiency, while external auditing expresses an opinion on the fairness of financial statements.
Internal Audit Objectives, Differences between internal and external auditing
- Review internal controls
- Assess risk management
- Identify areas for improvement
External Audit Objectives
- Express an opinion on the financial statements
- Ensure compliance with accounting standards
- Identify potential financial risks
2. Roles and Responsibilities of Internal and External Auditors
Internal Auditors
- Report to management and the audit committee
- Provide assurance on internal controls
- Make recommendations for improvement
External Auditors
- Independent and objective
- Issue audit reports expressing an opinion
- Limited authority and access to information
3. Methodology and Techniques
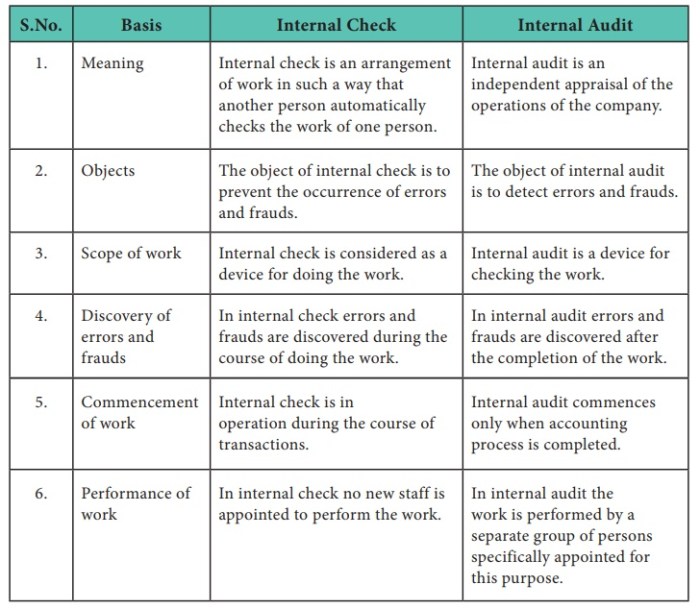
Internal Auditors
- Risk assessments
- Process reviews
- Data analytics
External Auditors
- Financial statement analysis
- Analytical procedures
- Sampling
External audits provide a higher level of assurance than internal audits.
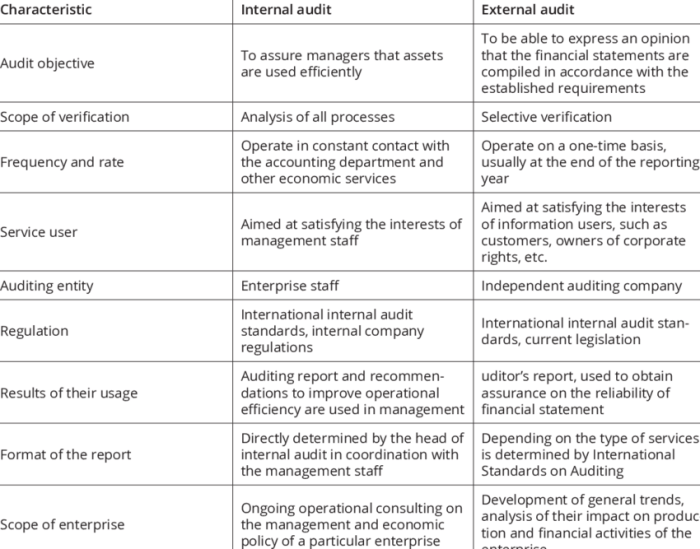
4. Reporting and Communication

Internal Auditors
- Management letters
- Audit reports
External Auditors
- Auditor’s opinion
- Management’s responsibilities
Internal audit reports are primarily used within the organization, while external audit reports are distributed to shareholders and other stakeholders.
5. Ethical Considerations: Differences Between Internal And External Auditing
Ethical Principles
- Integrity
- Objectivity
- Confidentiality
Conflicts of Interest
Internal auditors may face conflicts of interest due to their close proximity to the organization.
Independence and Objectivity
External auditors must maintain independence and objectivity to ensure the impartiality of their opinions.
FAQ Resource
What is the primary difference between internal and external auditing?
Internal auditing focuses on improving an organization’s operations and efficiency, while external auditing emphasizes expressing an opinion on the fairness of financial statements.
Who are the primary users of internal and external audit reports?
Internal audit reports are primarily used by management and those charged with governance, while external audit reports are primarily used by shareholders, creditors, and other external stakeholders.
What are the ethical considerations for internal and external auditors?
Both internal and external auditors must adhere to ethical principles and codes of conduct to ensure their independence, objectivity, and integrity.