Testout 15.1 build a computer from scratch – Embark on an educational journey with Testout 15.1: Build a Computer from Scratch. This guidebook provides a step-by-step roadmap for assembling and configuring your own personal computer, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to create a customized machine tailored to your specific needs and preferences.
Delve into the intricacies of computer architecture, exploring the essential components and their functions. Master the art of assembling hardware, ensuring proper handling and installation to avoid potential issues. Navigate the complexities of operating system installation, driver management, and BIOS configuration for optimal performance.
Components of a Computer

A computer system comprises a set of interconnected components that work together to process, store, and retrieve data and perform calculations. These components include the following:
- Processor (CPU):The central processing unit is the brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
- Memory (RAM):Random access memory stores data and instructions that are currently being processed by the CPU.
- Storage (HDD/SSD):Hard disk drives or solid-state drives store data and programs permanently.
- Motherboard:The motherboard connects all the components of the computer and provides a communication pathway between them.
- Power supply unit (PSU):The PSU provides electrical power to all the components of the computer.
- Graphics card (GPU):The GPU handles the processing of graphics and video data.
- Input/Output (I/O) devices:These devices, such as keyboards, mice, and monitors, allow users to interact with the computer and display information.

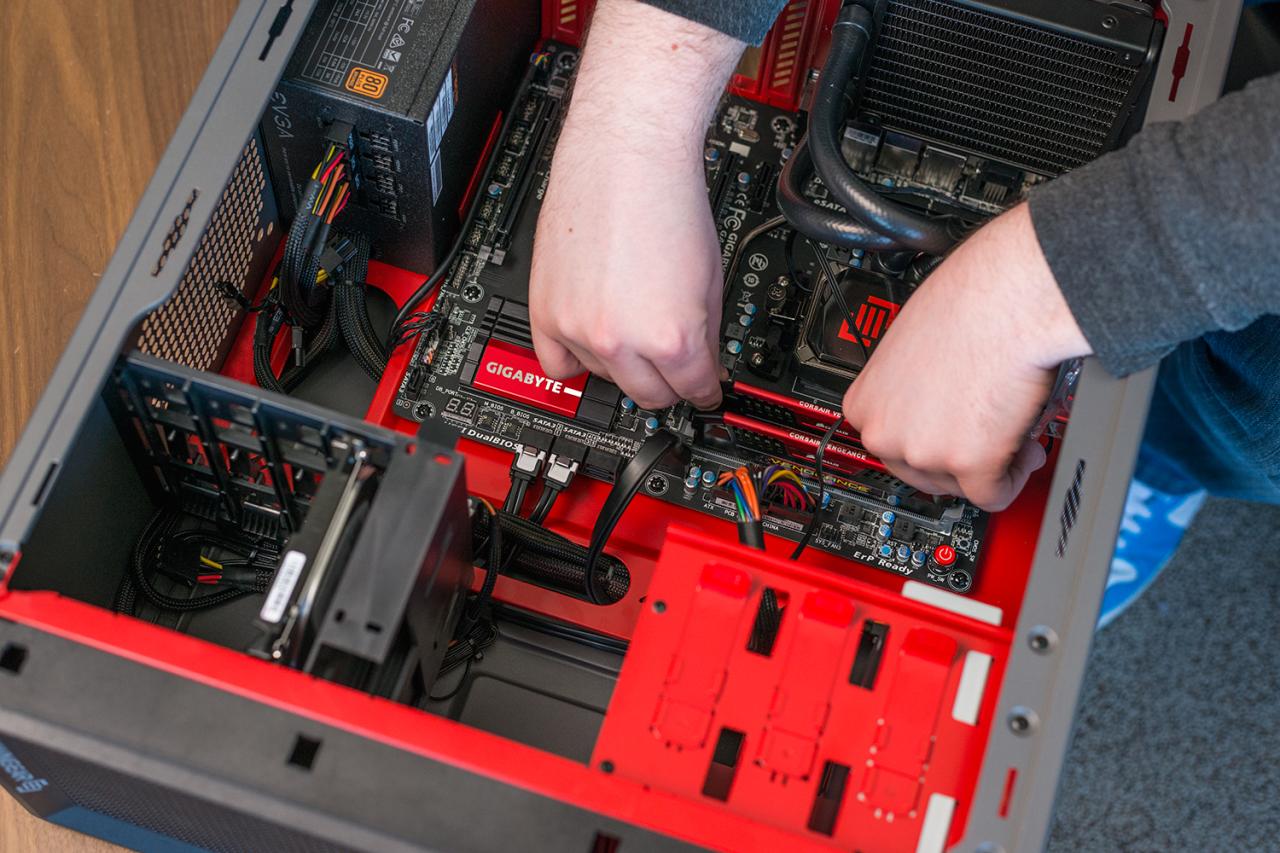
Assembling the Hardware
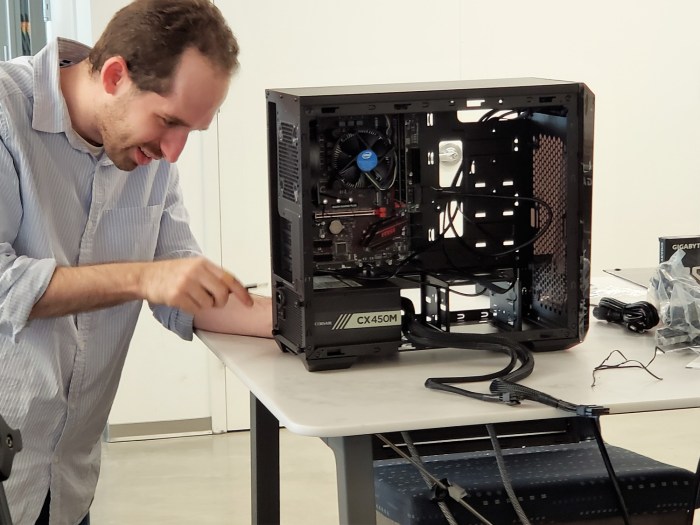

Assembling a computer requires careful handling and attention to detail. The following steps provide a general guideline for assembling a computer:
- Install the CPU:Carefully align the CPU with the socket on the motherboard and secure it with the lever or clamp.
- Install the RAM:Align the RAM modules with the slots on the motherboard and press down on both ends until they click into place.
- Install the storage device:Connect the HDD or SSD to the motherboard and secure it in the designated bay.
- Install the motherboard:Place the motherboard in the computer case and secure it with screws.
- Install the power supply unit:Mount the PSU in the case and connect it to the motherboard and other components.
- Install the graphics card:Insert the graphics card into the PCIe slot on the motherboard and secure it with screws.
- Install the I/O devices:Connect the keyboard, mouse, and monitor to the appropriate ports on the back of the computer.
Troubleshooting tips:
- Ensure all components are securely connected and properly seated.
- Check for bent or damaged pins on the CPU or RAM.
- Reset the CMOS settings on the motherboard if the computer fails to boot.
Installing the Operating System
An operating system (OS) is a software that manages the hardware and software resources of a computer. Common types of operating systems include Windows, macOS, and Linux.
To install an operating system:
- Create a bootable USB or DVD using the OS installation files.
- Boot the computer from the bootable media.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to select the installation options and create partitions on the storage device.
- Once the installation is complete, the computer will reboot into the new OS.
Drivers:
Drivers are software that allows the operating system to communicate with specific hardware devices. It is important to install the correct drivers for all the hardware components in your computer to ensure proper functionality.
Configuring the BIOS
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a firmware that initializes the hardware components of a computer and loads the operating system. It provides a set of options to configure the hardware settings and optimize performance.
To access the BIOS:
- Restart the computer.
- Press the designated key (usually Del or F2) to enter the BIOS setup.
In the BIOS settings, you can:
- Change the boot order of devices.
- Enable or disable hardware components.
- Adjust the clock speed and voltage of the CPU.
- Set the virtual memory settings.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance

Computers are prone to various problems that can affect their performance and functionality. Common problems include:
- Boot issues:Computer fails to start or boot into the operating system.
- Hardware failures:Malfunctioning components, such as the motherboard, CPU, or RAM.
- Software issues:Corrupted operating system files, viruses, or malware.
- Overheating:Excessive heat buildup can cause system instability and damage components.
- Check for loose connections or damaged components.
- Run diagnostics tests to identify hardware issues.
- Use antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and remove infections.
- Monitor system temperatures and ensure proper ventilation.
- Regularly clean the computer and its components to prevent dust accumulation.
- Update the operating system and software to fix bugs and security vulnerabilities.
- Back up important data to prevent loss in case of hardware failure.
- Changing the case:Choose a case that suits your aesthetic preferences and provides adequate cooling.
- Adding RGB lighting:Install LED strips or fans to create a unique visual experience.
- Upgrading hardware:Replace or add components, such as a faster CPU, more RAM, or a dedicated graphics card, to improve performance.
- Compatibility:Ensure that the new components are compatible with your motherboard and other hardware.
- Performance:Research the performance benchmarks of different components to make informed decisions.
- Cost:Set a budget for upgrades and compare the cost-benefit ratio of different options.
Troubleshooting procedures:
Preventative maintenance:
Customizing and Upgrading
Computers can be customized and upgraded to meet specific needs and enhance performance. Customization options include:
Considerations for upgrading:
Answers to Common Questions: Testout 15.1 Build A Computer From Scratch
What are the essential components of a computer system?
The essential components of a computer system include the motherboard, processor, memory, storage, graphics card, power supply, and case.
How do I install an operating system?
To install an operating system, you will need to create a bootable USB drive or DVD, insert it into your computer, and follow the on-screen instructions.
What is the purpose of the BIOS?
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is responsible for initializing and configuring hardware components during the boot process.