Welcome to our in-depth guide to the factor label method worksheet with answers. This resource provides a comprehensive overview of the factor label method, its applications, and a range of practice problems with step-by-step solutions. Whether you’re a student looking to master this essential technique or an educator seeking engaging materials, this worksheet is designed to empower you with the knowledge and skills you need to excel in dimensional analysis.
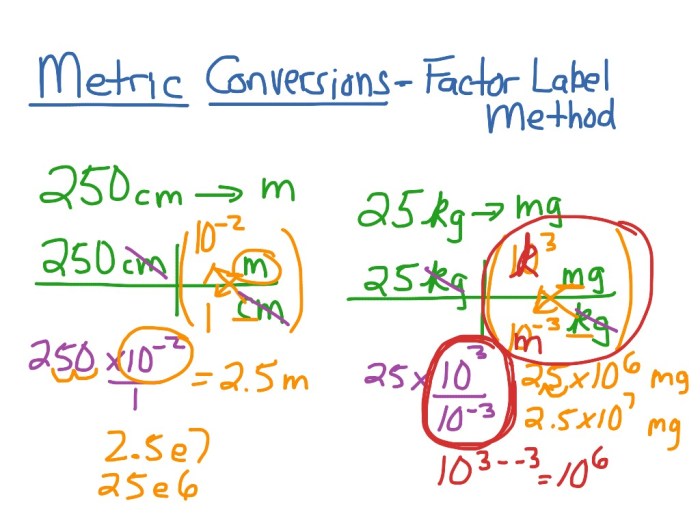
The factor label method, also known as dimensional analysis, is a powerful tool for converting units and solving real-world problems involving measurement. This worksheet delves into the fundamental principles of dimensional analysis, guiding you through the process of setting up and solving problems with confidence.
Our curated selection of problems covers a variety of scenarios, ensuring that you gain a thorough understanding of the method’s versatility.
Factor Label Method: Factor Label Method Worksheet With Answers
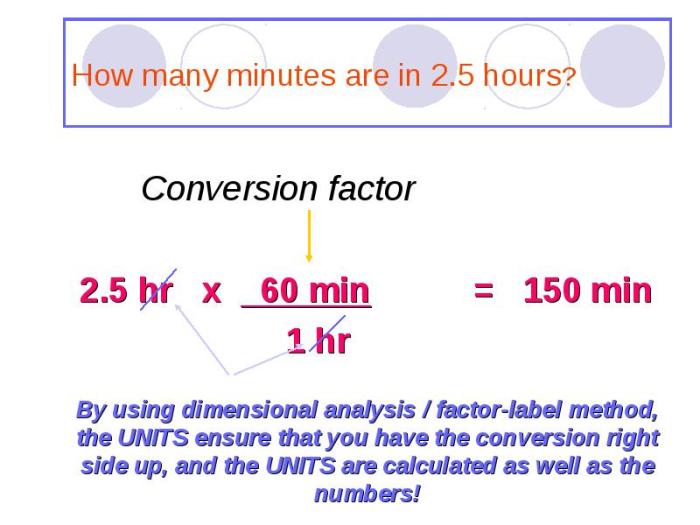
The factor label method, also known as dimensional analysis, is a technique used to convert units of measurement by multiplying and dividing by appropriate conversion factors.
The concept of dimensional analysis is based on the principle that an equation must balance in terms of its units as well as its numerical values.
Applications of the Factor Label Method, Factor label method worksheet with answers
- Converting units within the same measurement system (e.g., miles to kilometers)
- Converting units between different measurement systems (e.g., gallons to liters)
- Solving problems involving rates and proportions
- Calculating quantities in chemical reactions
Worksheet with Answers
| Problem | Setup | Solution | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convert 50 miles to kilometers | 50 miles x (1.609 kilometers / 1 mile) | 50 x 1.609 = 80.45 kilometers | 80.45 kilometers |
| Convert 2 gallons to liters | 2 gallons x (3.785 liters / 1 gallon) | 2 x 3.785 = 7.57 liters | 7.57 liters |
| Find the speed of a car traveling 60 miles per hour in kilometers per hour | 60 miles per hour x (1.609 kilometers / 1 mile) | 60 x 1.609 = 96.54 kilometers per hour | 96.54 kilometers per hour |
Examples
The factor label method can be used in a variety of real-world scenarios, such as:
- Calculating the amount of paint needed to cover a room
- Determining the fuel efficiency of a car
- Converting cooking recipes from one measurement system to another
Methods
To use the factor label method, follow these steps:
- Identify the initial and desired units.
- Find a conversion factor that relates the initial units to the desired units.
- Multiply the initial value by the conversion factor.
- The result will be the converted value in the desired units.
Procedures
When converting units using the factor label method, it is important to:
- Use the correct conversion factors.
- Multiply and divide correctly.
- Pay attention to the units of the answer.
Common errors to avoid include:
- Using the wrong conversion factors
- Multiplying or dividing incorrectly
- Ignoring the units of the answer
Conversion Factors
The following table provides a list of common conversion factors:
| Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| Length | 1 mile = 1.609 kilometers |
| Volume | 1 gallon = 3.785 liters |
| Speed | 1 mile per hour = 1.609 kilometers per hour |
FAQ Insights
What is the factor label method?
The factor label method, also known as dimensional analysis, is a technique for converting units by multiplying and dividing by fractions that are equal to one. This allows you to cancel out unwanted units and arrive at the desired unit.
How do I use the factor label method?
To use the factor label method, follow these steps: 1) Identify the given quantity and the desired unit. 2) Set up a fraction with the given quantity as the numerator and the desired unit as the denominator. 3) Multiply and divide by fractions that are equal to one to cancel out unwanted units.
What are some common applications of the factor label method?
The factor label method can be used to solve a variety of problems involving unit conversion, such as converting miles to kilometers, gallons to liters, or pounds to kilograms.